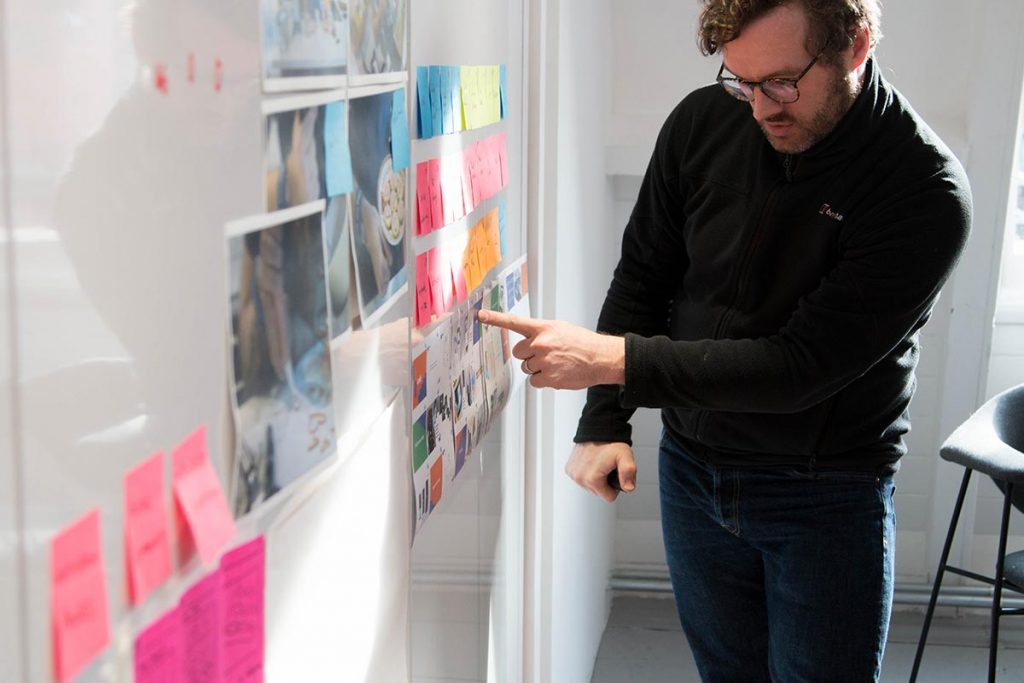
There are many factors that constitute a successful user interview, from building rapport to making sure you’ve got the right kind of person there.
However, once the participant is there in front of you with a cup of tea (whether that’s through a screen or in person), then your research questions become the most important thing of all.
A user interview is probably one of the most qualitative methods you can use in research. It allows you to understand the reasons behind certain behaviours, rather than just recognising the behaviours through quantitative methods.
Asking the right questions is the key to getting the most out of your research – and it’s not just about the context. How you word your questions could be the difference between gathering vague insights or covering an entire wall with sticky notes.
From our experience with user interviews at Code, we’ve pulled together some top tips to help you ask the right questions to your participants.
Avoid asking leading questions
During everyday conversations, many of us won’t think twice about using leading questions (the kind of questions that may prompt someone to answer in a certain way). They’re a natural part of our day-to-day chat and we often say them without much thought or conscious intent.
Therefore, refraining from asking leading questions in a user interview is probably going to feel unnatural and awkward at first (we’ve all slipped up at some point at Code!). It just takes time and practice.
These are the kind of questions that could prompt a biased response:
How easy is it to find what you’re looking for?
By referencing the word ‘easy’, this question could predispose participants to think that it should be easy, therefore swaying their response.
A better question would be, “What would you be looking for on this page?”
Would you choose the first option?
Naturally, people often prefer to say ‘yes’ to something when it appears that this is the preferred option. If you focus on the ‘first option’ as the facilitator, then the participant may believe that this is the implied ‘correct’ answer.
A less-biased question would be, “How would you proceed?”
Be impartial
Avoiding leading questions is just one part of being impartial. It’s also best to avoid sharing your own experiences with the participant, as this may encourage them to answer the question slightly differently.
A bit of casual sharing during the introduction stage is fine (we are humans after all!).
Refer back to your research aims
It’s a good idea to have your research aims to hand during the session, regardless of how many times you’ve read them before. The physical act of referring back to them will help you to check if you’ve covered the right questions.
To establish our research aims at Code, we use this simple framework:
We are researching… [a product/journey]
For… [user demographic]
So that… [achievement or outcome]
Here’s an example:
We are researching… people’s experiences of different working environments
For… people who work in or are looking to work in tech
So that… we can create a working environment that attracts the best talent
Don’t be limited by your script
Preparing a script is one of the best ways to ensure that you ask the right questions and achieve your research aims from the session.
However, there’s no such thing as a user interview that perfectly follows a script (how boring would that be?). The unpredictable nature of participant insights may force you to deviate down an unexpected path and ask a few different questions.
This isn’t a bad thing – unless you veer off course completely and can’t find your way back! Think of your script like an elastic band – you can pull away slightly, but you’ll need to pull back eventually or else the elastic band will snap.
Use probes to gather further insights
Probing is an established research technique that can help you to gather more information from your participants.
Sometimes, a participant may tell you one thing but actually mean another. Or, they might tell you about what they did but not about why they did it. Using the right probe can help you to dig a little deeper.
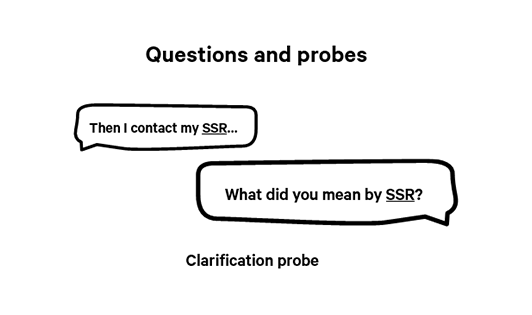
Clarification probe
Clarification probes are useful when:
- The participant’s answer was unclear or ambiguous
- The participant is discussing a sensitive subject (this may make it harder for them to articulate what they want to say)
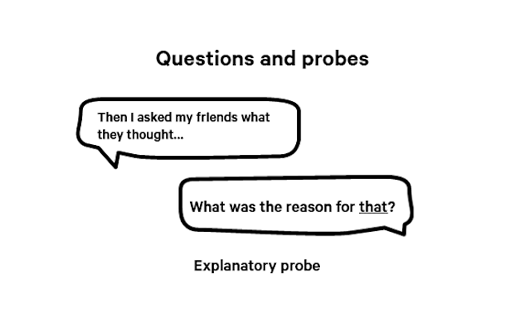
Explanatory probe
Explanatory probes are useful when:
- You want to understand what motivates your participant to do things
- You want to understand the impact something had on the participant
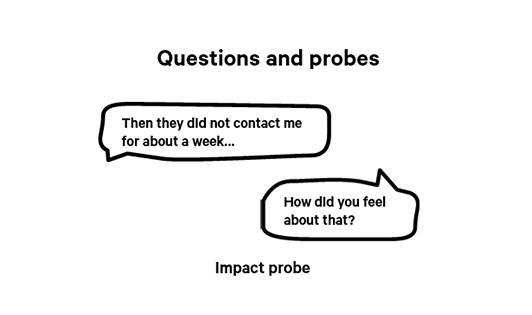
Impact probe
Impact probes are useful when:
- You want to find out more about the participant’s emotional response
- You want the participant to elaborate further about an experience
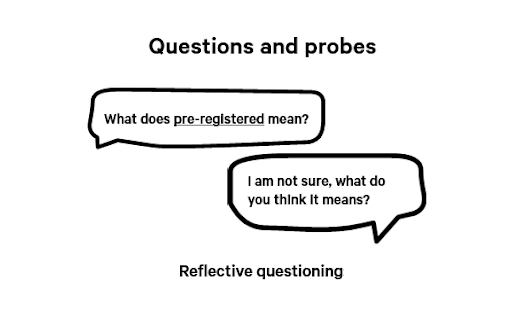
Reflective probe
Reflective probes are useful when:
- You want to clarify the participant’s understanding without any bias
- You want to encourage the participant to elaborate without your input
Challenging probe
Challenging probes are useful when:
- You want to ensure that there are no inconsistencies in what the participant has told you
- You think the participant may be confused by what you’re asking or testing

Just to recap…
- Avoid asking leading questions
- Be impartial
- Refer back to your research aims
- Don’t be limited by your script
- Use probes to gather further insights
Mastering all of the above largely comes with experience and even then, it’s natural to slip up occasionally. A user interview is probably one of the most personal research methods you can use and despite its intent, will always be conversational. Therefore, it’s never a failure if you ask a leading question or share your own bias – rather, you should recognise when it happens and be conscious of it in the next interview.
Need help your vision or product strategy? We’d love to hear from you.